The translational level (
TL) of a mRNA transcript in a RPD is defined as the average
NRPKM (normalized reads per kilobase per million mapped reads) value of its coding region (CDS) in that RPD and calculated by the following formula
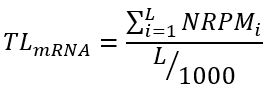
where
L is the length (in bps) of the coding region and
i is the
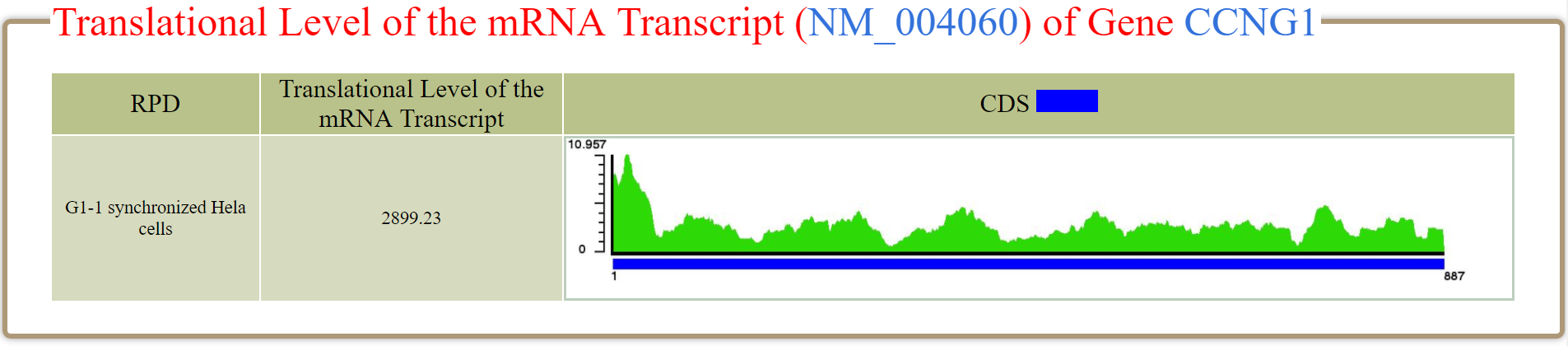
i-th position of the coding region. For example, in RPD (G1-1 synchronized Hela cells), the
TL of NM_004060 (one mRNA isoform of the gene CCNG1) is 2899.23 where
L=887.
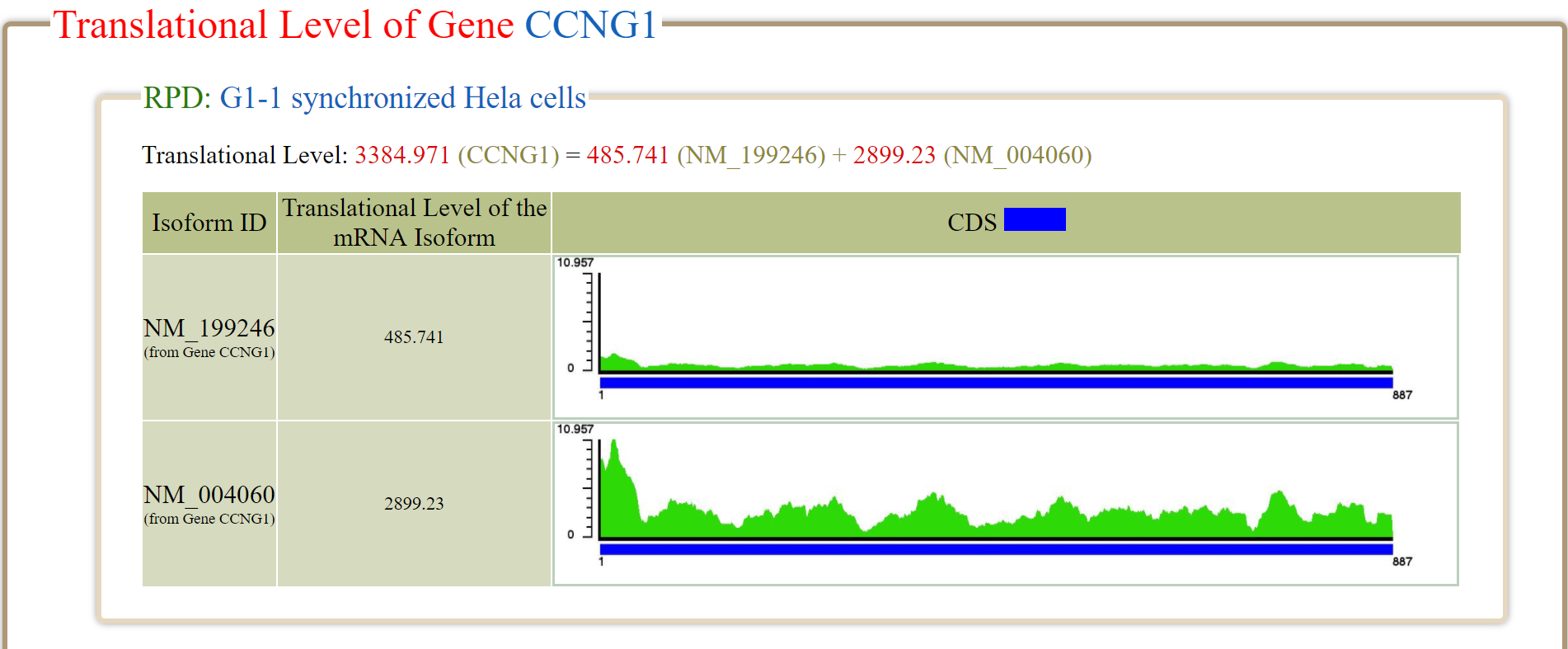
The translational level of a gene (denoted as
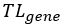
) in a RPD is defined as the sum of the translational levels of all its mRNA isoforms in that RPD. For example, the gene
CCNG1 has two mRNA isoforms (NM_199246 and NM_004060). In RPD (G1-1 synchronized Hela cells), the
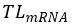
of NM_199246 and
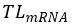
of NM_004060 are 485.741 and 2899.23, respectively. Therefore, the
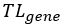
of
CCNG1 is 3384.971 which equals the sum of 485.741 and 2899.23.